Business & Tech Essentials

ZATCA E-Invoicing Phase 2 Integration Explained
Digital transformation in Saudi Arabia has reached a new stage with the implementation of ZATCA E-Invoicing Phase 2. The initiative led by the Zakat, Tax and Customs Authority (ZATCA) aims to standardize how businesses issue, verify, and store invoices electronically. For every registered organization, this system ensures transparency, accuracy, and real-time compliance in financial reporting.
As the Integration Phase begins, businesses must connect their invoicing systems directly with ZATCA’s Fatoora portal to validate invoices automatically. This change not only eliminates manual reporting but also builds a unified tax infrastructure across all industries.
For companies seeking a dependable technical bridge, TrackAcc by Out2Sol Global, a platform developed on Microsoft technologies, provides secure integration with ZATCA’s system. It helps organizations generate, verify, and store compliant e-invoices while maintaining data accuracy and operational efficiency.
What Is ZATCA E-Invoicing and Why It Matters
ZATCA, the Zakat, Tax and Customs Authority, introduced electronic invoicing (E-Invoicing) under its national system called Fatoora. The goal is to replace paper-based invoicing with a secure digital process that improves transparency, reduces tax evasion, and supports Saudi Arabia’s move toward digital governance.
Under this framework, every business registered for VAT must issue and store invoices electronically through systems that can connect to ZATCA’s central platform. The process ensures each invoice is digitally signed, validated, and traceable.
In ZATCA E-Invoicing, every transaction passes through a secure verification process. Businesses must issue invoices in specific formats such as XML or PDF/A3 with embedded XML data. These formats help ZATCA read, validate, and store invoice information automatically. The system also supports real-time monitoring, ensuring that all tax submissions follow official regulations without manual uploads.
The Shift from Phase 1 to Phase 2 – What Changed 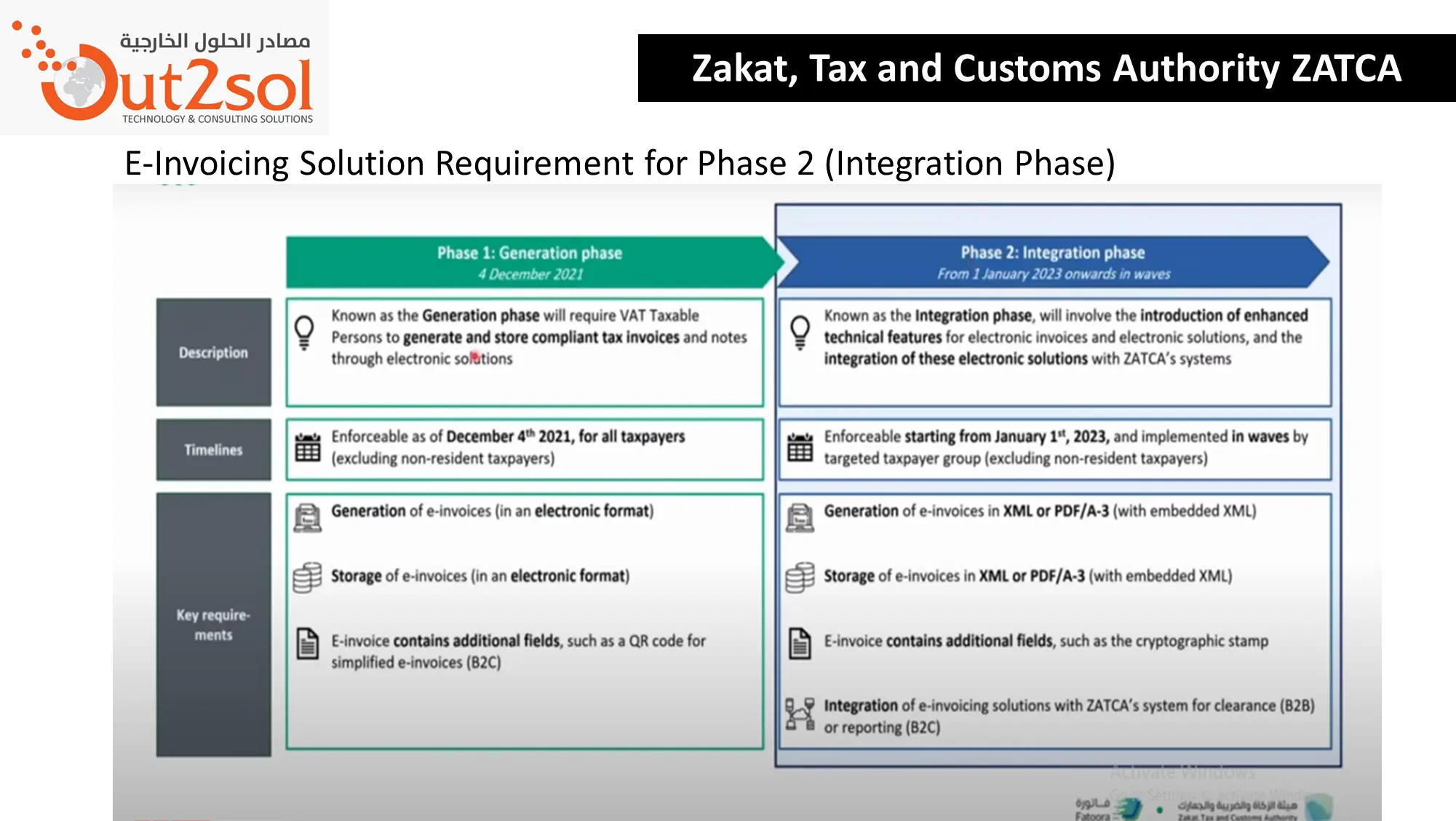
When ZATCA launched Phase 1 in December 2021, it focused mainly on digital invoice generation and recordkeeping. Businesses were required to issue e-invoices through a compliant system but without any direct system-to-system communication with ZATCA servers.
However, Phase 2, known as the Integration Phase, introduced a significant change. It connects business systems directly with ZATCA through APIs for real-time validation. Once an invoice is created, it is automatically sent to ZATCA’s Fatoora portal, where it is validated, time-stamped, and returned with a digital signature.
This integration eliminates manual submissions and improves compliance accuracy. Each invoice must include a unique identifier (UUID), a hash code, and a QR code generated according to ZATCA’s rules. The authority can instantly verify these details, reducing fraud and simplifying auditing.
Phase 2 also introduced invoice classification, separating B2C, B2B, and B2G transactions. Businesses now need to ensure their systems can handle multiple invoice types, each with slightly different data and QR code fields.
For example:
-
B2C invoices must always include a QR code for consumer validation.
-
B2B invoices require submission to ZATCA for clearance before being shared with clients.
This phase ensures digital invoice consistency across all business sectors in Saudi Arabia.
ZATCA E-Invoicing News 2026: Mandatory Deadlines & Requirements
Stay ahead of regulatory changes and avoid non-compliance penalties with the latest ZATCA e-invoicing 2026 news, specifically targeting smaller revenue thresholds and integration deadlines. So what is it:
-
Wave 23 Deadline (March 31, 2026): Businesses with annual VATable revenues exceeding SAR 750,000 in 2022, 2023, or 2024 must complete their Fatoora platform integration by this date.
-
Wave 24 Deadline (June 30, 2026): For the first time, the threshold has dropped to SAR 375,000, bringing thousands of SMEs into the mandatory Phase 2 scope.
-
Penalty Waiver Extension: ZATCA has extended the "Initiative to Cancel Fines and Exempt Taxpayers from Penalties" until June 30, 2026. This offers a vital grace period for businesses to correct past errors without financial hits.
-
Mandatory Technical Standards: All 2026 waves must issue invoices in XML or PDF/A-3 format, featuring a cryptographic stamp and a UUID (Unique Universal Identifier).
-
6-Month Warning Rule: ZATCA continues to provide at least six months' notice before a taxpayer's specific integration date, allowing time for sandbox testing and API configuration.
-
Real-Time Reporting Requirement: Phase 2 mandates that B2B invoices be cleared in real-time by ZATCA, while B2C (simplified) invoices must be reported within 24 hours of issuance.
Key Requirements for ZATCA Phase 2 Integration
To achieve full compliance, organizations must prepare both their technical infrastructure and regulatory documentation before integrating with ZATCA’s Fatoora system.
1. System and Technical Readiness
Your invoicing or ERP software must be capable of generating invoices in XML or PDF/A3 with embedded XML formats. These formats allow automated reading and verification by ZATCA servers. From your internal documentation, the integration setup typically includes:
-
A Microsoft .NET–based application environment
-
A SQL Database for structured storage
-
API endpoints that communicate directly with ZATCA for invoice submission and clearance
Each invoice must contain essential fields such as invoice number, customer VAT number, and total amount. Data validation happens instantly through API communication.
2. Cloud and Network Configuration
Before integration, ZATCA requires that your server IP addresses be whitelisted to enable secure communication with the Fatoora portal. Cloud servers, such as Microsoft Azure or AWS, are generally used to store and transmit invoices securely.
Your setup should also include:
-
Encrypted connections for API calls
-
Cloud backup for XML and PDF copies
-
Access control for administrators and auditors
3. Registration and Compliance Documentation
Before integration testing, companies must have:
-
A valid VAT registration
-
A Commercial Registration (CR) certificate
-
A Fatoora account created on the ZATCA platform
After registration, ZATCA provides API credentials and simulation account access to test invoice submission before going live. Once verified, businesses can move from simulation to production, ensuring their data flow and invoice formats meet compliance standards.
4. Invoice and Data Management
The system must generate unique invoice identifiers, digital signatures, and timestamps to match ZATCA’s authentication model.
Additionally, businesses should maintain:
-
Real-time reporting dashboards
-
Reconciliation tools to verify cleared invoices with ZATCA data
-
Audit-ready storage for all issued invoices
These measures ensure continuous compliance and simplify the annual VAT audit process.
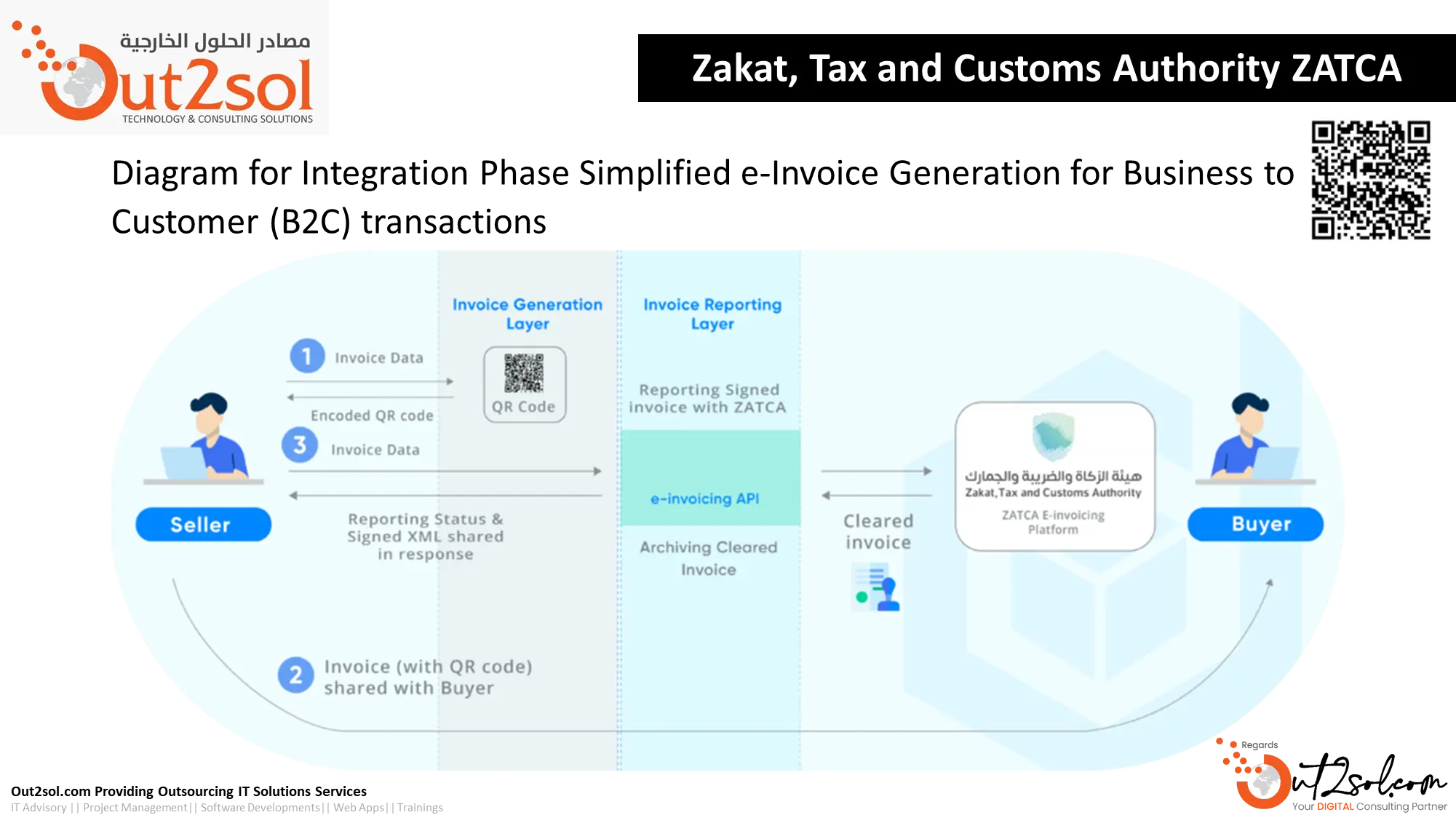
How the ZATCA API Integration Process Works
During Phase 2 of ZATCA E-Invoicing, every approved business system must communicate directly with the authority through a secure Application Programming Interface (API). The process begins when an invoice is generated in the organization’s ERP or accounting software. That invoice, structured in XML or PDF/A3 with embedded XML, is transmitted instantly to the Fatoora portal for clearance.
-
Invoice Generation: The ERP creates a digital invoice with seller VAT number, buyer details, total amount, and timestamp.
-
API Transmission: Through ZATCA’s REST-based API endpoints, data is securely sent for verification.
-
Validation and Stamping: ZATCA verifies the invoice, adds a unique identifier (UUID) and hash value, and returns a digitally signed copy.
-
Storage and Sharing: The verified invoice is stored in the business system and shared with the buyer.
For real-time invoice clearance, the API must be active throughout working hours and support both instant and bulk submissions, depending on transaction volume.
Developers typically rely on Microsoft C# frameworks within the .NET environment to manage these integrations because the Fatoora API documentation provides direct support for Microsoft libraries and security protocols.
QR Code Structure and Invoice Verification
A critical addition in Phase 2 is the expanded QR code. It allows ZATCA and end users to validate invoices easily. Every code is automatically generated through the invoicing system and must contain specific data fields defined in ZATCA’s electronic invoice resolution:
-
Seller name
-
Seller VAT number
-
Timestamp of invoice issuance
-
Total amount including VAT
-
VAT amount
-
Invoice hash value
-
UUID (unique invoice ID)
For B2C invoices, QR codes are mandatory in both Phase 1 and Phase 2. For B2B and B2G transactions, they became mandatory only after Phase 2 integration.Scanning the code allows buyers and regulators to confirm authenticity instantly, reducing fraud and duplicate reporting.
In practice, the QR code is generated automatically through the same Microsoft-based integration logic that sends XML data to ZATCA. The code is then embedded in PDF/A3 invoices shared with customers.
Data Formats and Cloud Storage Compliance
ZATCA E-Invoicing Phase 2 requires strict adherence to data structure and storage standards. Invoices must be stored electronically for at least six years and remain accessible for audit and regulatory verification.
Accepted Formats
-
XML: Primary machine-readable format for ZATCA validation.
-
PDF/A3 with embedded XML: Human-readable copy containing embedded machine data.
These formats ensure each invoice can be re-validated if requested by ZATCA auditors.
Cloud and Backup Practices
Enterprises use cloud environments such as Microsoft Azure, AWS, or Google Cloud for secure invoice retention. Your Out2Sol framework recommends dual storage: primary cloud hosting plus a local backup for business continuity during connectivity issues. Each invoice file is timestamped and encrypted. Access control is limited to authorized finance and audit staff, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality.
Role of TrackAcc in ZATCA E-Invoicing Integration
TrackAcc, developed by Out2Sol Global, acts as a unified back-office platform tailored for ZATCA Phase 1 and Phase 2 compliance. It is built on the Microsoft .NET framework with a SQL database foundation, allowing direct API communication with ZATCA’s Fatoora portal.
Integrated Modules
-
Central Billing and Tax Management: All sales and purchases pass through a single ZATCA-compliant workflow.
-
Inventory and Supply Chain Control: Material requests, purchase orders, and goods receipts link directly to invoice creation.
-
CRM and POS Integration: Customer data and point-of-sale transactions automatically generate digital invoices for ZATCA clearance.
-
Analytics and Reconciliation: TrackAcc offers real-time invoice tracking and automated Excel exports to cross-check ZATCA submissions with local records.
By using TrackAcc, businesses gain an auditable trail for every transaction and minimize manual errors in tax filing. The system’s architecture supports instant and bulk invoice submission modes, making it suitable for schools, retailers, and large organizations managing high invoice volumes.
Challenges Businesses Face During Phase 2 Integration
While the shift to digital invoicing brings long-term benefits, many organizations encounter technical and operational challenges during Phase 2.
1. API Connectivity and Testing
Errors often arise from misconfigured API credentials or server whitelisting. ZATCA provides a simulation environment to test API calls before production, but incomplete testing may cause submission failures.
2. Data Mapping and Validation
Some legacy ERP systems lack fields needed for XML invoices. Developers must map each data field (VAT numbers, totals, and hash values) to match ZATCA requirements.
3. Cloud Security and Compliance
Maintaining data sovereignty is critical. Invoices must be stored within approved cloud regions to comply with Saudi data laws.
4. Operational Change
Teams require training to handle new reporting formats and monitor daily submissions. Automation reduces manual work but needs ongoing oversight.
Addressing these challenges early helps ensure uninterrupted invoice validation and regulatory trust.
Readiness Checklist for ZATCA E-Invoicing Phase 2
-
Verify VAT registration and CR certificate.
-
Obtain ZATCA API credentials and set up Fatoora accounts.
-
Ensure server IP whitelisting and firewall permissions.
-
Configure invoice formats (XML and PDF/A3).
-
Test invoice submission in the simulation environment.
-
Review daily reports and reconciliation logs.
-
Train finance and IT teams on compliance procedures.
Following this checklist ensures organizations are technically and legally ready for Phase 2 rollout.
The Future of Digital Taxation and E-Invoicing in 2026
ZATCA’s digital tax framework continues to guide Saudi Arabia toward a fully automated economy in 2026. The integration phase has laid the groundwork for real-time analytics, automated tax reporting, and smarter compliance monitoring.
New integration waves planned for 2026 will bring more sectors under ZATCA’s e-invoicing system and strengthen cross-platform verification. Check out the latest news and updates here.
These 2026 milestones represent ZATCA's most significant push yet into the SME sector, requiring high-speed API connectivity for real-time clearance. Businesses already using TrackAcc or similar Microsoft-based solutions are well positioned for these updates, as their systems align with ZATCA’s evolving roadmap. Sustaining data accuracy and secure cloud management will remain vital for long-term compliance.
Final Insight
ZATCA E-Invoicing Phase 2 Integration is not just a technical project; it is a regulatory framework that redefines how businesses in Saudi Arabia manage transactions and report taxes. With the right tools, such as Microsoft-based integration solutions and TrackAcc’s ZATCA-compliant platform, organizations can ensure accuracy, efficiency, and trust in every invoice they issue.
Crucially, the "Initiative to Cancel Fines" has been extended until June 30, 2026, offering a final opportunity for businesses to integrate and correct past errors without financial penalties. As ZATCA moves toward pre-filled VAT returns, early adoption of a robust solution like TrackAcc is the best way to safeguard your business and ensure seamless compliance before these final 2026 deadlines.